Irched chafaa

PhD. in Telecommunication, Paris-Saclay University, France.
IBM Data Science professional certificate.
View My LinkedIn Profile
List of Publications
Summary
Researcher at the intersection of machine learning and wireless communications, with expertise in optimization, deep learning, and distributed learning for next-generation networks developed through PhD and postdoctoral projects. Skilled in Python, MATLAB, and AI-driven modeling, with a solid publication record and experience in interdisciplinary collaboration.
Selected projects
Hybrid Tree-Transformer Model for Power Optimization
This project introduces a hybrid Tree-Transformer model for efficient per-user power optimization in wireless networks. By compressing user features into a single root and applying a Transformer only to this representation, the model achieves scalable inference with minimal computational cost. Experiments show it delivers near-optimal performance while significantly reducing runtime compared to standard full-attention approaches.
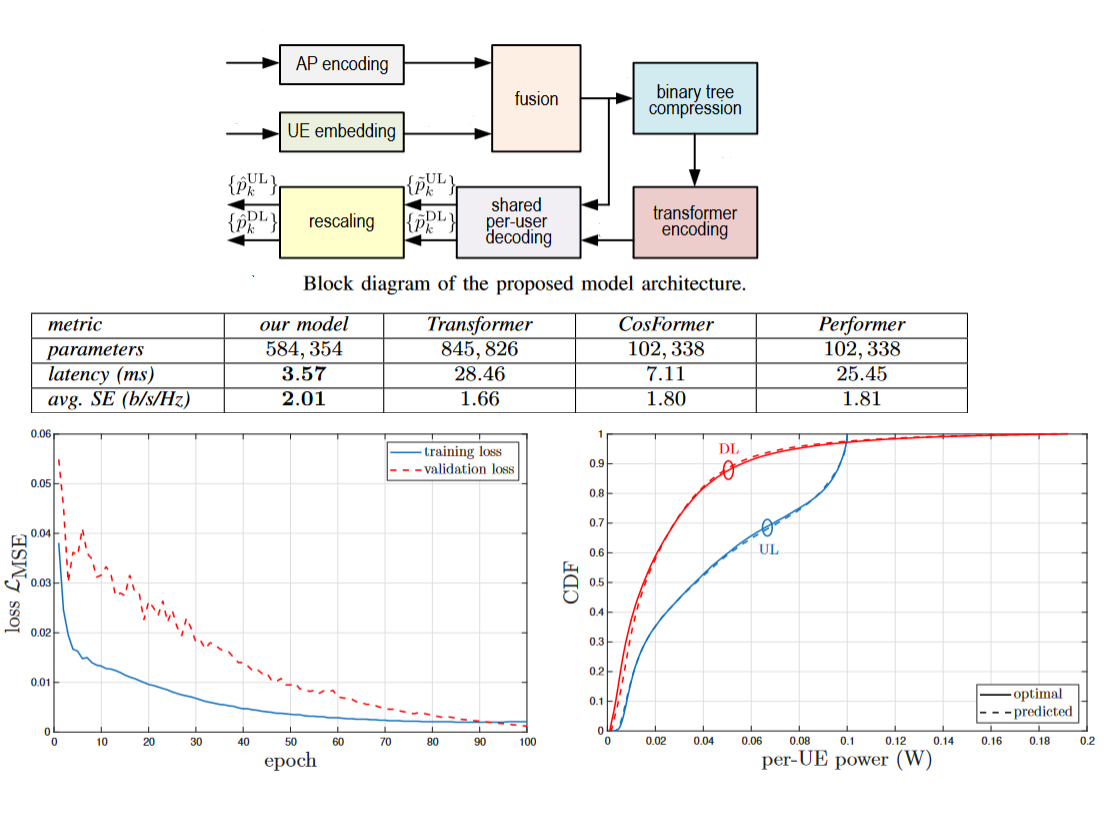
Modified CosFormer for Users Association and Power Allocation
This project presents a lightweight Transformer model for joint AP clustering and power allocation in user-centric cell-free massive MIMO systems. Unlike existing approaches, the model handles dynamic network configurations without channel estimation and eliminates pilot contamination through smart AP-user assignment. A customized linear attention mechanism efficiently captures user-AP interactions, achieving linear scalability with the number of users. Experiments demonstrate near-optimal performance in maximizing minimum spectral efficiency, combining adaptability, efficiency, and robustness in dynamic wireless scenarios.

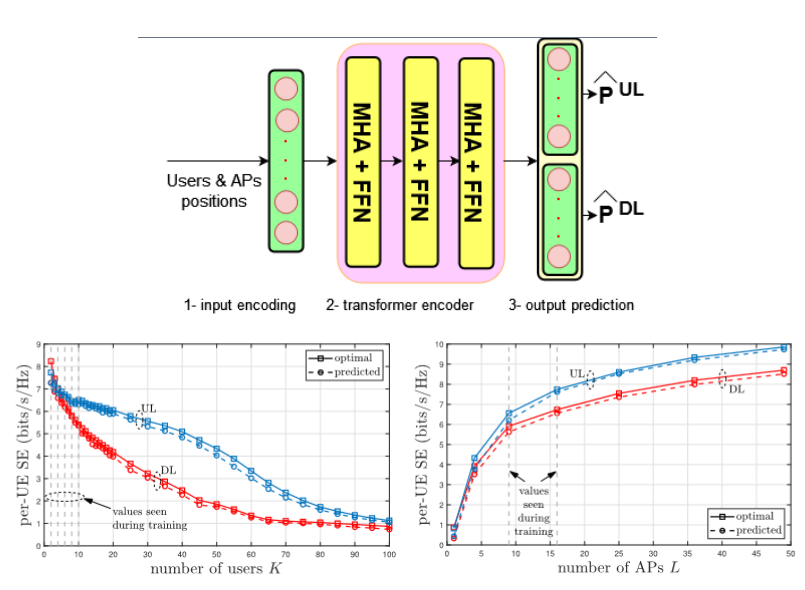
Transformer model for flexible power optimization (Supervised Learning)
The transformer model is trained to predict optimal powers (Uplink and Downlink jointly) for wireless networks using the positions of users and transmitters as input information. The transformer architecture allows to handle varying input sizes to handle the dynamic nature of wireless networks with varying user loads and active transmitters. The trained model provides optimal power performance, but with less computational complexity and input information compared to the traditional optimization methods.
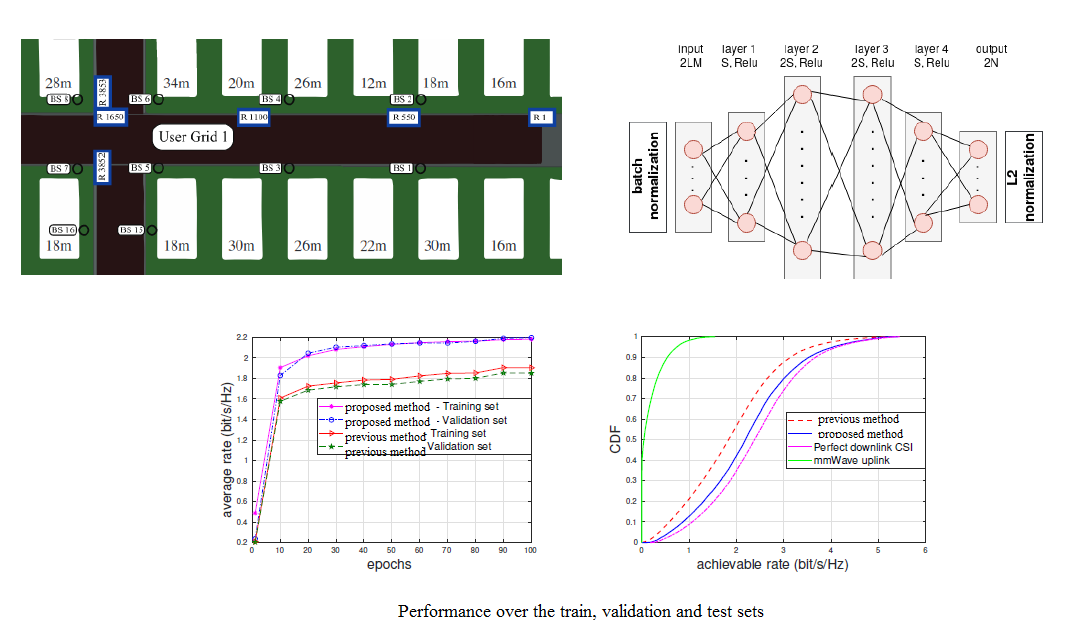
Self-supervised deep learning for beam prediction in mmWave networks
Beam prediction in dynamic mmWave networks is a challenging task. In this project, self-supervised deep learning is leveraged to predict, based on sub-6 GHz channels data, mmWave beams in one access-point/receiver link and optimize the data rate. The trained neural network exploits the sub-6 GHz channel data at the input to output directly the beamforming vector for the mmWave band.
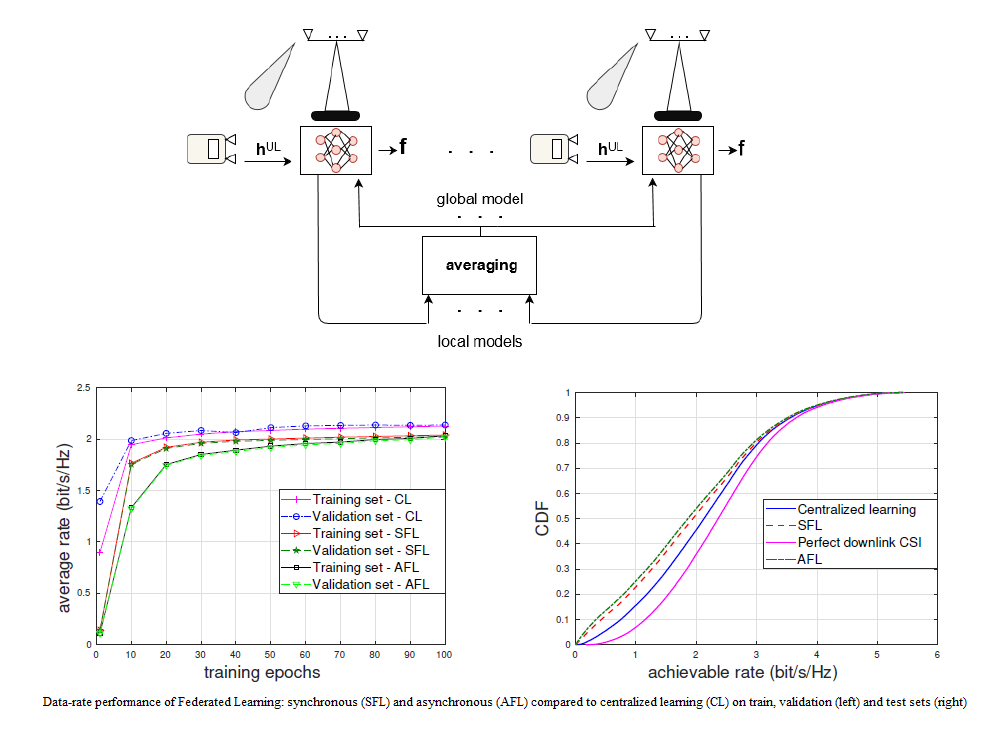
Federated Learning for beam prediction in multi-link mmWave networks
In a multi-link network, a federated learning scheme is proposed to predict the mmWave beamforming vectors locally, at each access-point. Federated learning consists in sharing local models with a server, which can aggregate them into a more informed global model for all links, leading to better performance without sharing their local data. In this project, we investigate both synchronous and asynchronous modes of uploading of the local models, and compare their performance to centralized learning.
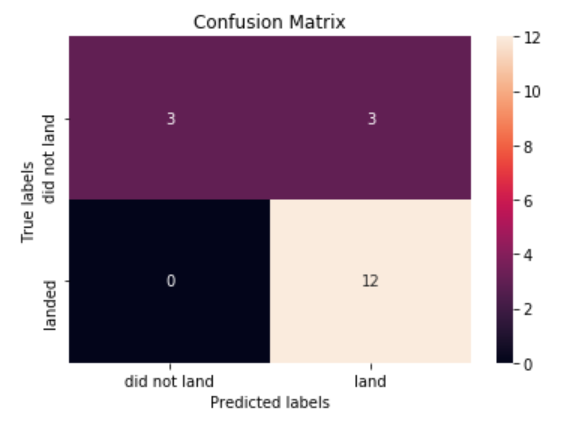
SpaceX Falcon 9 first stage Landing Prediction
This project is the final project of the IBM Data Science professional certificate on Coursera. It exploits machine learning tools to predict if the Falcon 9 first stage will land successfully. The project involves collecting data, Exploratory Data Analysis, data vizualisation, feature engineering, SQL queries and prediction using different estimators. The machine learning pipeline allows to predict the sucess of the first stage landing, which reduces the launch cost.
Page template forked from evanca










